By Dr. Amornrat Limmanee, Solar Photovoltaic Team Leader of Solar Photovoltaic Research Team,Energy Innovation Research Group of ENTEC Interviewed by Dr. Buncha Thanaboonsombut Article by Mrs. Orawan Sumriddetkajorn
ถาม: ขอทราบประวัติการศึกษาของ ดร.เบนซ์ ครับ ทราบมาว่าไปเรียนที่ประเทศญี่ปุ่นตั้งแต่ชั้นมัธยมศึกษาตอนปลาย?
ตอบ:
หลังจากจบการศึกษาระดับมัธยมศึกษาตอนต้นก็สอบชิงทุนรัฐบาลเพื่อไปศึกษาต่อที่ประเทศญี่ปุ่น โดยไปเรียนภาษาญี่ปุ่นก่อน 1 ปี จากนั้นก็เข้าศึกษาในระดับมัธยมศึกษาตอนปลายจนกระทั่งจบปริญญาเอกทางด้านอิเล็กทรอนิกส์เชิงกายภาพ (physical electronics) รวมระยะเวลา 13 ปีค่ะ
เนื่องจากทุนที่ได้รับเปิดกว้าง ไม่ได้ระบุว่าต้องไปศึกษาทางด้านไหน แต่ด้วยความที่ชอบวิชาวิทยาศาสตร์และคณิตศาสตร์ อีกทั้งการได้ไปเรียนที่ประเทศญี่ปุ่น ซึ่งมีความเจริญทางด้านไฟฟ้าและอิเล็กทรอนิกส์อยู่แล้ว และเมื่อได้เรียนก็ยิ่งทำให้รู้สึกว่าเราน่าจะเหมาะกับด้านนี้จึงเลือกเรียนวิศวกรรมไฟฟ้าค่ะ
ถาม: เหตุใดจึงเลือกศึกษาลงลึกเรื่องเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ตอนที่เรียนปริญญาโท-เอกครับ?
ตอบ:
ถาม: ช่วงที่เรียนปริญญาเอกหัวข้องานวิจัยที่ศึกษาลงลึกเกี่ยวกับอะไร และได้ฝึกงานกับบริษัทเอกชนที่ไหนบ้างครับ?
ตอบ:
เป็นการพัฒนาชั้นฟิล์มในเซลล์ชนิดผลึกซิลิคอน ซึ่งเป็นชั้นกันการสะท้อนและลดการสูญเสียพลังงานด้านขั้วด้านล่างกับด้านบนโดยการสร้างซิลิคอนไนไตรด์ (silicon nitride) เนื่องจากเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ต้องการให้แสงหักเหเข้ามากก็ต้องพัฒนาชั้นบนให้ลดการสะท้อนและลดการสูญเสียด้านอื่นด้วยจึงพัฒนาฟิล์มซิลิคอนไนไตรด์ และฟิล์มซิลิคอนออกไซด์ (silicon-oxide) เพื่อใช้ในโครงสร้างเซลล์ชนิดผลึกซิลิคอนค่ะ
ตอนฝึกงานได้ฝึกที่บริษัท มิตซูบิชิ อิเล็คทริค โดยเรียนรู้ตั้งแต่การทำวิจัยและพัฒนาในเซลล์เล็ก การวัดวิเคราะห์เซลล์เล็กไปจนถึงกระบวนการสร้างจริงว่ากว่าจะมาเป็นแผงเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ที่วางจำหน่ายมีขั้นตอน และมีกระบวนการอะไรบ้าง
บริษัทในเครือ มิตซูบิชิ อิเล็คทริค นอกจากจะผลิตอุปกรณ์ไฟฟ้าอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ต่างๆ แล้วยังมีโรงผลิตเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ด้วย แต่ส่วนใหญ่จำหน่ายภายในประเทศและส่งออกไปประเทศอื่นที่ไม่ใช่ประเทศไทย ในตอนนั้นเขาวัดคุณสมบัติแผ่นซิลิคอนเวเฟอร์เพื่อศึกษาว่าเวเฟอร์แบบไหนที่เหมาะจะมาสร้างเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ วิธีการคัดเลือก การวิเคราะห์ว่าทำอย่างไรให้ได้ประสิทธิภาพสูงและมีการสูญเสียตรงไหนบ้าง ซึ่งญี่ปุ่นจะลงในรายละเอียดมาก
ถาม: เนื่องจากประเทศญี่ปุ่นมีความโดดเด่นด้านการผลิตอุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์และเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์มาก ถ้ามองภาพรวมของประเทศญี่ปุ่นเทียบกับโลกมีการแข่งขันกับประเทศไหนเป็นพิเศษไหมครับ?
ตอบ:
ถาม: เวลาพูดถึงเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์คนทั่วไปจะนึกถึงแผงสีดำที่ติดตั้งบนหลังคาบ้าง หรือบนพื้นบ้าง ช่วยให้ภาพรวมของเทคโนโลยีเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ว่าหัวใจของเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ประกอบด้วยอะไรบ้างครับ?
ตอบ:
A solar cell l is a semiconductor with energy band gaps that directly absorb the solar spectrum. There are various types of solar cells, but the most common is fabricated from silicon for its affordable prices and large quantities. However, some types are rare, e.g., those made for rare earth, which is expensive and has high production cost. The doped material creates a potential difference in the PN junction, the photon [1] creates the negatively charged electron and the positively charged hole, both of them could conduct electricity. A potential difference, therefore, causes the electrons to move in the opposite direction of the hole, and when a circuit is complete, electricity is generated.
[1] โฟตอน (photon) เป็นอนุภาคของแสง พลังงานของโฟตอนจะแตกต่างกันตามความยาวของคลื่นแสง
ถาม : ในการทำงานของเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ ทีมวิจัยมองแสงเป็นคลื่นหรือเป็นอนุภาคครับ?
ตอบ:
It can be viewed both ways. If we talk about an electron and a hole, then we consider light as particles because, in solar cell measurements, one need to measure quantum efficiency [2] to see how much light is converted into electricity at each wavelength. On the contrary, if we consider light as wave, the amount of light energy per square meter before conversion will be of interest in order to see the whole picture.
[2] ประสิทธิภาพควอนตัม (quantum efficiency) ปริมาณอิเล็กตรอนที่วัสดุปล่อยออกมาต่อปริมาณโฟตอนที่ใส่เข้าไป
ถาม : ระบบของเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ต้องมีอุปกรณ์หลักอะไรบ้างครับ?
ตอบ:
- แผงเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์
คือการนำเซลล์หลายตัวมาต่อกัน เมื่อเป็นแผงก็จะมีแผงหลายแผงมาต่อกันเพื่อกำหนดค่าแรงดันและกระแสที่เหมาะสมกับระบบ
- อินเวอร์เตอร์ (inverter)
เนื่องจากไฟฟ้าจากเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์เป็นไฟฟ้ากระแสตรง ถ้าจะใช้กับอุปกรณ์บ้านก็ต้องมีอินเวอร์เตอร์ (inverter) เพื่อแปลงไฟฟ้ากระแสตรงเป็นกระแสสลับก่อน
- แบตเตอรี่
นอกจากนี้ ไฟฟ้าที่ผลิตจากเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ไม่สามารถเก็บในตัวเองได้ ต้องปล่อยออกไปเลย ดังนั้น ถ้าต้องการเก็บไฟฟ้าต้องเก็บในแบตเตอรี่
- ตัวควบคุมการชาร์จ (charge controller)
นอกจากนี้ ไฟฟ้าที่ผลิตจากเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ไม่สามารถเก็บในตัวเองได้ ต้องปล่อยออกไปเลย ดังนั้น ถ้าต้องการเก็บไฟฟ้าต้องเก็บในแบตเตอรี่ เมื่อมีตัวเก็บไฟแล้วก็ต้องมีตัวควบคุมการชาร์จ (charge controller) ด้วย เพราะไฟจากเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์อาจไม่สม่ำเสมอเปลี่ยนแปลงตามค่าแสงอาทิตย์ ซึ่งอาจสร้างความเสียหายต่อแบตเตอรี่ได้ถ้าชาร์จโดยตรง
ถาม : ถ้าพูดถึงเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์จะเป็นวัสดุที่รับแสงเข้ามาแล้วเปลี่ยนเป็นกระแสไฟฟ้า แต่ถ้ามองทั้งระบบเรียกโซลาร์โฟโตวอลเทอิก (solar photovoltaic system) ใช่ไหมครับ?
ตอบ:
ใช่ค่ะ จริงๆ การผลิตไฟฟ้าจากแสงอาทิตย์จะมีอีกรูปแบบหนึ่งคือ การใช้เป็นความร้อน (solar thermal) ผลิตน้ำร้อนหรือไอน้ำแล้วไปปั่นไฟ แต่ถ้าแปลงจากแสงเป็นไฟฟ้าโดยตรงจะเรียก solar photovoltaic system หรือ solar PV system
ถาม: ในมุมมองของวัสดุที่พูดถึงผลึกแบบต่างๆ เช่น ผลึกเดี่ยว (monocrystalline) พหุผลึก (polycrystalline หรือ multicrystalline) อสัณฐาน (amorphous) ผลึกเหล่านี้ส่งผลต่อประสิทธิภาพของโฟโตวอลเทอิกที่แตกต่างกันอย่างไรครับ?
ตอบ:
ผลึกที่ทำให้โฟโตวอลเทอิกมีประสิทธิภาพสูงที่สุดคือผลึกเดี่ยวเพราะเป็นเนื้อเดียว แต่มีราคาสูง ถ้าเป็นพหุผลึกหรือหลายผลึกจะมีเกรนต่างๆ ทำให้มีรอยต่อระหว่างเกรน ซึ่งมีโอกาสที่จะสูญเสียพลังงานได้มาก เดิมทีผลึกเดี่ยวมีราคาสูงจึงพบวัสดุประเภทพหุผลึกหรือหลายผลึกในท้องตลาดมากกว่าแม้จะมีประสิทธิภาพต่ำกว่า แต่ถ้ามองในแง่เศรษฐศาสตร์ก็จะคุ้มค่ากว่า
ปัจจุบันจีนผลิตผลึกเดี่ยวได้ถูกลงจนมีราคาพอๆ กับพหุผลึก ทำให้สัดส่วนในตลาดที่แท้จริงตอนนี้มีผลึกเดี่ยวมากกว่า ซิลิคอนเวเฟอร์ที่ใช้ในอุตสาหกรรมเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ร้อยละ 96 ผลิตที่จีน ทำให้จีนสามารถคุมได้ตั้งแต่ต้นน้ำถึงปลายน้ำทำให้ราคาลดต่ำลงเรื่อยๆ ตั้งแต่ปี 2553 จากเดิมราคาต่อวัตต์ของเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สูงประมาณ 80 บาทต่อวัตต์ ตอนนี้ลงมาเหลือ 20 บาทต่อวัตต์ ถ้าในระดับโซลาร์ฟาร์มต่ำกว่า 10 บาทต่อวัตต์ ดังนั้นต้นทุนพลังงานแสงอาทิตย์จะลดต่ำลงสาเหตุมาจากราคาแผงต่ำลง ประเทศอื่นไม่สามารถลดราคาลงได้เท่าจีน เพราะจีนคือผู้ผลิตเวเฟอร์ เมื่อนำไปขายต่อจะเป็นผู้กำหนดราคาและควบคุมคุณภาพได้หมด
ถาม: การแข่งขันของเทคโนโลยีฟิล์มบางซิลิคอนอสัณฐาน (amorphous silicon) เป็นอย่างไรครับ?
ตอบ:
ถาม: ถ้าอุปสงค์ลดลง การวิจัยและพัฒนายังคงดำเนินต่อไหมครับ หรือลดลงไปตามตลาด?
ตอบ:
ถาม: งานวิจัยที่ทำตอนอยู่ที่ศูนย์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์และคอมพิวเตอร์แห่งชาติ (NECTEC) เกี่ยวกับอะไรครับ?
ตอบ:
ถาม: เมื่อผลึกมีราคาลดลง ต้องมีการปรับเปลี่ยนทิศทางการวิจัยอย่างไรครับ?
ตอบ:
ช่วงนั้นมีโอกาสได้ไปอบรมการวิเคราะห์สมรรถนะและความน่าเชื่อของแผงเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ที่ AIST (The National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology) ประเทศญี่ปุ่น ซึ่ง AIST ถือว่าเป็น 1 ใน 3 ของศูนย์ทดสอบเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ที่ใหญ่ที่สุดในโลก เขาสอนตั้งแต่การวัดสเปกตรัมแสง เพราะมีผลกระทบต่อประสิทธิภาพของเซลล์แต่ละชนิด เช่น เซลล์ชนิดนี้ทำงานที่เยอรมนีได้ดี แต่ที่ญี่ปุ่นอาจไม่ดีเท่าที่คิด และยังมีปัจจัยอื่นๆ เช่น อุณหภูมิ รวมถึงการวัดในห้องปฏิบัติการต้องวัดอะไรบ้าง การวัดระบบที่เป็นแผงใช้งานจริงบริเวณภายนอก ตามมาตรฐานต้องมีอะไร ใช้เครื่องมืออะไร ซึ่งทำให้ได้เรียนรู้มากขึ้น
ถาม: ถ้ามีแผงเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ติดตั้งภายนอก ปัจจัยทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา เช่น มีเมฆมาบัง มีลมพัด ปัจจัยสำคัญอะไรบ้างที่ต้องคำนึงถึงครับ?
ตอบ:
อันดับแรกคือค่าความเข้มแสง อันดับที่สองคืออุณหภูมิแผง เพราะเงื่อนไขมาตรฐานวัดที่ค่าความเข้มแสง 1000 W/m22 อุณหภูมิแผงที่ 25°C เพื่อแสดงว่ากำลังการผลิตไฟฟ้าของแผงกี่วัตต์ สำหรับประเทศไทยอุณหภูมิแผงที่ตั้งเฉยๆ ก็ 30°C เมื่อรับแสงอุณหภูมิจะสูงขึ้นอีก ยิ่งช่วงเมษายนบางครั้งอุณหภูมิแผงสูงถึง 70°C และถ้าติดตั้งบนหลังคา ซึ่งการระบายอากาศไม่ดีก็มีโอกาสที่อุณหภูมิจะสูงถึง 80°C แม้ว่าเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์จะชอบแสง แต่ไม่ชอบความร้อนค่ะ
ถาม: สภาวะที่เหมาะสมของเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ชนิดผลึกเดี่ยวต้องเป็นอย่างไรครับ?
ตอบ:
สภาวะที่เหมาะสมคือมีความเข้มแสงสูงแต่อุณหภูมิต่ำ น่าจะเป็นแถบยุโรปบางเมือง แต่ในเขตร้อนแถบเส้นศูนย์สูตรแสงเยอะตลอดทั้งปี ข้อดีคือได้รับแสง แต่ต้องยอมรับว่าจะมีการสูญเสียที่เกิดจากอุณหภูมิได้เช่นเดียวกัน
ถาม: การที่เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์มีสีเข้ม มีเหตุผลทางวิชาการไหมครับว่าทำไมต้องมีสีแบบนี้?
ตอบ:
สีเข้มจะดูดกลืนแสงขาวได้ทั้งหมด การที่เราเห็นสีไหนหมายความว่าสีนั้นจะสะท้อนเข้าตาเรา คือไม่ถูกดูดกลืน เช่น ซิลิคอนที่เราเห็นเป็นสีน้ำเงินเข้ม เพราะสะท้อนสีน้ำเงินเข้มออกมาแล้วดูดกลืนสีช่วงอื่น จริงๆ แล้วพลังงานแสงอาทิตย์ร้อยละ 40 อยู่ที่แสงขาวที่มีความยาวคลื่นตั้งแต่ 400-800 นาโนเมตร
เราสามารถปรับสีของเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ได้เพื่อความสวยงาม เช่น เซลล์ชนิดผลึกซิลิคอน ถ้าปรับชั้นซิลิคอนไนไตรด์ที่เป็นชั้นกันสะท้อนด้านบน โดยปรับค่าดัชนีหักเหของแสงกับความหนาของฟิล์มก็จะสามารถปรับสีให้เป็นสีเหลือง สีแสด สีอื่นๆ ได้ แต่ต้องแลกกับประสิทธิภาพของแผงที่ลดลง เพราะแผงจะดูดกลืนสีนี้น้อยลง
งานวิจัยด้าน BIPV (Building Integrated Photovoltaic) สามารถทำให้เลือกได้ว่าต้องการเซลล์สีอะไร กระจกสีอะไร จะไม่เน้นเรื่องประสิทธิภาพ แต่เน้นที่ความสวยงามสำหรับใช้ตกแต่งเป็นหลักค่ะ
ถาม: ในแง่ทฤษฎีสามารถทำให้เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์มีประสิทธิภาพสูงสุดได้เท่าไหร่ครับ?
ตอบ:
ถ้าเป็นเซลล์แบบประเภทรวมแสง คือ นำเลนส์มารวมความเข้มแสง มีประสิทธิภาพใกล้เคียงร้อยละ 50 บางครั้งจะเห็นข่าวรายงานว่าเซลล์ชนิดนี้มีประสิทธิภาพร้อยละ 49-50 ถ้าไปอ่านรายละเอียดและเงื่อนไขในการทดสอบจะพบว่าเป็นเซลล์รวมแสง 300 ซัน ซึ่งแสงทั่วไปคือ 1 ซัน หมายความว่าเซลล์ชนิดนี้รวมความเข้มแสง ณ จุดพื้นที่ที่โฟกัสแล้ววัดประสิทธิภาพตรงจุดนี้ ซึ่งเงื่อนไขนี้จะไม่เกิดในธรรมชาติแต่ในแง่ทฤษฎีหรือสภาพแวดล้อมที่ควบคุมสามารถทำได้ แต่ในความเป็นจริงประสิทธิภาพการทำงานจะไม่ถึงเพราะมีปัจจัยทางอุตุนิยมวิทยาเข้ามาเกี่ยวข้อง
ถาม: ในทางปฏิบัติประสิทธิภาพอยู่ประมาณเท่าไหร่ครับ?
ตอบ:
ถ้าเป็นเซลล์ซิลิคอนทั่วไปประสิทธิภาพจะประมาณร้อยละ 20 แต่ถ้าเป็นประสิทธิภาพแผงที่ใช้ในโซลาร์ฟาร์มปัจจุบันจะอยู่ประมาณร้อยละ 18-19
ถาม: มีความหวังด้านเทคโนโลยีที่จะผลักดันประสิทธิภาพให้สูงมากกว่านี้ไหมครับ?
ตอบ:
ในแง่ประสิทธิภาพของเซลล์ซิลิคอนมีความเป็นไปได้ที่จะทำได้ถึงร้อยละ 25-26 แต่ราคาจะสูงตามไปด้วย ดังนั้น คนจะไม่ลงทุนทำโซลาร์ฟาร์มด้วยแผงที่ประสิทธิภาพสูงสุดแต่จะพิจารณาความคุ้มค่าในการลงทุน เนื่องจากเมื่อพิจารณาในแง่เศรษฐศาสตร์แล้วพบว่าประสิทธิภาพสูงใช้พื้นที่น้อยกว่าเท่านั้น ส่วนแผงประสิทธิภาพต่ำก็สามารถผลิตได้เท่ากันเพียงแต่ใช้พื้นที่มากกว่าเท่านั้น
ถาม: เราได้ยินเทคโนโลยีเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์มานานแล้ว อีกทั้งเคยมีนักวิชาการบางท่านเสนอนำเข้าระบบกริด โดยมีความฝันว่าคนจำนวนมากในประเทศจะผลิตไฟฟ้าใช้กันเอง แต่การใช้งานในปัจจุบันยังมีแค่เพียงบางบ้านไม่กระจายไปทั่ว ทั้งนี้มีอุปสรรคอะไรครับ?
ตอบ:
สาเหตุที่เทคโนโลยีเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ยังไม่มีการใช้งานกันทั่วไปในวงกว้าง เนื่องจากเป็นระบบการผลิตไฟฟ้าที่ไม่เสถียร กล่าวคือมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงไปตามสภาพอากาศ อีกทั้งในช่วงเวลากลางคืนก็ไม่สามารถผลิตกระแสไฟฟ้าได้ ซึ่งจะแตกต่างจากโรงไฟฟ้าอื่นที่สามารถควบคุมกำลังการผลิตได้ 24 ชั่วโมง ดังนั้น ต้องแก้ระบบให้มีความเสถียรก่อน เช่น อาจต้องใช้แบตเตอรี่มาเก็บสำรองไฟ ซึ่งก็จะทำให้ราคาต้นทุนสูงขึ้นจึงยังไม่เหมาะที่จะใช้เป็นระบบหลักในการผลิตกระแสไฟฟ้า
ถ้าเป็นระบบเล็ก ต้องสร้างความรู้และความเข้าใจในสิ่งที่เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ทำได้ก่อน เพราะความคาดหวังของคนคิดว่าถ้าติดแล้วจะสามารถใช้แทนไฟฟ้าทั้งบ้านได้ ซึ่งจริงๆ แล้ว แค่ช่วยลดปริมาณการใช้ไฟลงได้ ไฟฟ้าที่ผลิตจากเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สามารถใช้กับเครื่องไฟฟ้าทั่วไป เช่น พัดลม ไฟแสงสว่างได้ แต่ไม่เหมาะที่จะใช้กับเครื่องใช้ไฟฟ้าที่กินไฟ เช่น เครื่องปรับอากาศ เตารีด หรือเตาอบ
นอกจากนี้ราคาระบบเล็กอาจไม่ถูกนัก เพราะระบบต้องมีอินเวอร์เตอร์ ค่าติดตั้ง ค่าแผง ดังนั้น คนที่ติดตั้งต้องมีเงินระดับหนึ่งหรือเป็นคนที่อยากทดลองใช้จริงๆ และถ้าต้องการติดตั้งเชื่อมต่อกับสายส่งก็ต้องทำเรื่อง ยื่นเอกสารต่างๆ เพื่อแจ้งการไฟฟ้า ซึ่งก็จะมีขั้นตอนการดำเนินการอยู่ค่ะ
ถาม: ในภาพใหญ่ของประเทศไทยมีนโยบายที่อยากให้เพิ่มสัดส่วนการใช้ปริมาณไฟฟ้าจากเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์มากขึ้นไหมครับ?
ตอบ:
มีค่ะ แต่จะเน้นส่งเสริมการติดตั้งบนหลังคากับลอยน้ำ การที่ส่งเสริมให้ติดตั้งบนหลังคาบ้าน หลังคาโรงงาน หลังคาโกดังก็เพื่อจะได้ไม่รบกวนพื้นที่ดินสำหรับการเกษตร เป็นการใช้พื้นที่อาคารที่มีอยู่แล้วให้เกิดประโยชน์ ซึ่งส่วนหนึ่งรัฐสนับสนุน แต่ระยะหลังจะเป็นการติดตั้งบนหลังคาโกดังและโรงงานขนาดกลางและขนาดใหญ่เนื่องจากมีเงินทุน ถ้าขายไฟได้และลดพีกช่วงเวลากลางวันก็จะลดค่าไฟได้ทำให้คืนทุนได้เร็ว
ส่วนเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ลอยน้ำเป็นเทรนด์ใหม่ของทั่วโลก เป็นการใช้พื้นที่ผิวน้ำ เช่น ทะเล ทะเลสาบ เขื่อน โดยนำเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ไปติดบนทุ่น จากนั้นนำทุ่นไปลอยน้ำเพื่อใช้พื้นที่ให้เป็นประโยชน์ อีกแง่หนึ่งคืออุณหภูมิแผงจะเย็นกว่าเนื่องจากใกล้น้ำและมีลม
ประเทศไทยเริ่มติดตั้งแล้วที่เขื่อนสิรินธรของการไฟฟ้าฝ่ายผลิต (EGAT) โดยติดตั้งใช้จริง 45 เมกะวัตต์ แต่ก็ต้องศึกษากันในระยะยาว เพราะแผงอยู่ใกล้ความชื้นตลอดเวลาก็อาจทำให้อุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์เสื่อมสภาพ ถ้าติดตั้งใกล้ทะเลก็จะมีไอเกลือ ซึ่งจะมีผลเรื่องการกัดกร่อนบนตัวแผงและสายไฟค่ะ
ถาม: อายุการใช้งานของเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ประมาณกี่ปีครับ?
ตอบ:
ถ้าตัวแผงมีการรับประกันประมาณ 20-25 ปี สมรรถนะจะลดลงไม่ต่ำกว่าร้อยละ 80 จากตั้งต้น แต่ในเขตร้อนชื้นจะเสื่อมเร็วกว่า อายุการใช้งานจึงไม่ถึง 20 ปีแต่ถ้าคุ้มทุนแล้วก็ไม่เป็นปัญหาระยะเวลาที่คุ้มทุนสำหรับระบบใหญ่จะประมาณ 7 ปี แต่ถ้าเป็นระบบเล็กตามบ้านเรือนจะประมาณ 10 กว่าปี (ขึ้นกับขนาดระบบ ราคาอุปกรณ์ ราคาขายไฟ แรงจูงใจที่ได้รับ) อย่างไรก็ดี แม้ว่าเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์จะเสื่อมก็ยังสามารถผลิตไฟฟ้าได้ แต่อุปกรณ์ที่เสื่อมก่อนคือ อินเวอร์เตอร์
ถาม: ถ้าเปรียบเทียบราคาของอินเวอร์เตอร์เทียบกับราคาทั้งระบบคิดเป็นสัดส่วนเท่าไหร่ครับ?
ตอบ:
ประมาณร้อยละ 10 ค่ะ หรือประมาณหลักหมื่น ซึ่งสำหรับโรงงานไม่น่ามีปัญหา แต่สำหรับบ้านเรือนค่อนข้างมีผลกระทบสูงค่ะ
ถาม: มีวิธีการจัดการปลายทางแผงที่หมดอายุหรือมีประสิทธิภาพต่ำอย่างไรครับ?
ตอบ:
ถ้าในต่างประเทศจะมีโรงงานรีไซเคิลแผงคือ แยกแต่ละส่วนและนำกลับมาใช้ แต่ต้นทุนในการรีไซเคิลยังสูงมาก ไม่ว่าจะเป็นพลังงาน หรือสารเคมีที่ต้องใช้ เมื่อประเมินแล้วยังไม่ค่อยคุ้มทุนที่จะรีไซเคิล จึงใช้แนวทางในการใช้ซ้ำ
ในประเทศไทยยังไม่มีโรงงานรีไซเคิล และกลไกการใช้งานซ้ำก็ยังไม่มีแต่กำลังอยู่ระหว่างการพัฒนา ปัจจุบันเราติดตั้งแผงในระบบไปแล้วไม่น้อยกว่า 3 กิกะวัตต์หรือมีอยู่ไม่ต่ำกว่า 12 ล้านแผง ถ้าตามแผนอีก 10-20 ปี เราจะมีมากกว่า 40 ล้านแผง ดังนั้น การจัดการปลายทางอย่างเป็นระบบจะเป็นเรื่องสำคัญที่บอกว่าเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ดีต่อสิ่งแวดล้อมจริงหรือไม่
ถาม: ในต่างประเทศที่เจริญมากอย่างประเทศญี่ปุ่น เยอรมนี หรือประเทศอื่นในยุโรปเขามีวิธีจัดการเซลล์ที่หมดอายุอย่างไรครับ?
ตอบ:
รวบรวมกลับมาเพื่อรีไซเคิลค่ะ ที่นำหน้าที่สุดจะเป็นยุโรปที่สามารถรีไซเคิลได้ทุกส่วน ตั้งแต่กระจก ซิลิคอน ขั้วไฟฟ้า นำโลหะมีค่าออกมา ในตอนนี้อาจไม่คุ้มทุนแต่ในทางเทคนิคสามารถทำได้ จึงกลายเป็นว่าตอนนี้การแยกส่วนและบดทำลายเพื่อฝังกลบเป็นวิธีที่นิยมที่สุด ซึ่งประเทศไทยก็ใช้การฝังกลบเป็นหลักค่ะ
ถาม: อยากให้ ดร.เบนซ์ เล่าประสบการณ์ที่มีโอกาสได้ทำงานเชิงนโยบายเกี่ยวกับการใช้เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ครับ?
ตอบ:
ปัจจุบันโซลาร์ฟาร์มบางที่เปลี่ยนแผงโดยไม่รอถึง 20 ปี เนื่องจากเขาขายไฟ เมื่อพลังงานที่ผลิตได้ลดลงเขาก็เปลี่ยนแผงเพื่อรักษาสถานะการผลิตไฟฟ้า
At present, some solar farms replace solar panels before their lifetime of 20 years. They do this because the energy produced was reduced once the solar panels deteriote and by replacing them with new ones, they can maintain their status of power-generating enterprises.
แผงที่ถูกเปลี่ยนบางส่วนถูกเก็บไว้ บางส่วนถูกขายต่อ บางส่วนถูกบริจาคไป ซึ่งเราจะไม่ทราบปลายทางที่จะไปรวบรวมกลับมาจัดการได้เลย
ถาม: รายงานสถานภาพเมื่อ 10 ปีก่อน น่าจะมีการมองอนาคตข้างหน้าด้วย อนาคตที่คาดไว้เมื่อ 10 ปีก่อนกับสถานะในปัจจุบันสอดคล้องหรือแตกต่างกันอย่างไรครับ?
ตอบ:
สิ่งที่คาดไว้และตรงกับปัจจุบันคือจำนวนแผงเพิ่มขึ้นเรื่อยๆ ดังนั้นการจัดการจึงเป็นเรื่องที่สำคัญ เพราะเราพูดถึงการรีไซเคิลแผงตั้งแต่ 10 ปีที่แล้ว แต่ตอนนั้นยังถูกมองว่าอีกนานคือ 20-25 ปี เรายังไม่ต้องทำเรื่องนี้ก่อน ตั้งแต่ปี 2553 มีการพูดถึงงานวิจัยรีไซเคิลแต่ยังไม่ได้โฟกัสมาก เพราะไทยเน้นส่งเสริมการติดตั้งเพื่อใช้งานทั้งบนดิน หลังคา หรือลอยน้ำ แต่สุดท้ายแผงทั้งหมดคงต้องเข้าสู่กระบวนการจัดการและรีไซเคิลหรือทิ้ง แต่สิ่งที่กังวลคือ เมื่อต่างประเทศรื้อแผงจะส่งมาที่ประเทศไทยเหมือนกับอุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์หรือไม่
ถาม: การทำงานที่ผ่านมามีความภาคภูมิใจในเรื่องใดครับ?
ตอบ:
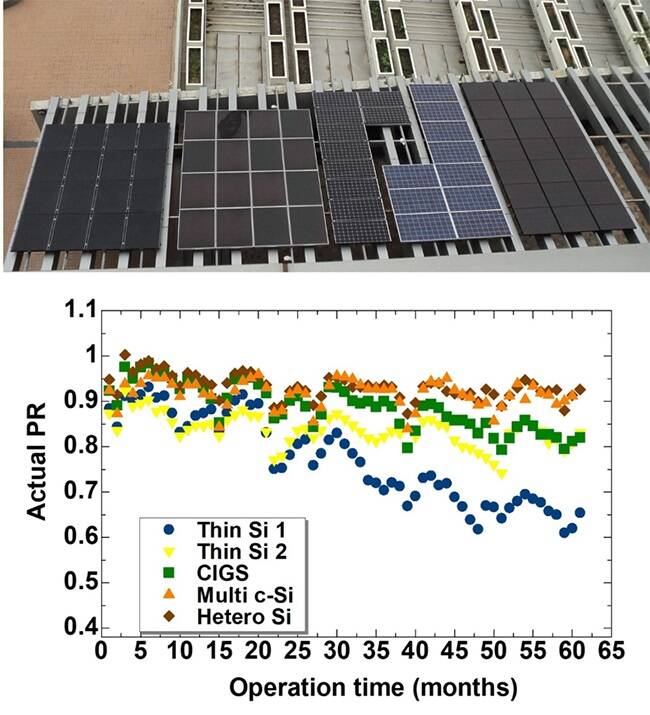
สิ่งที่ภูมิใจคือส่วนของการวิเคราะห์ทดสอบ เมื่อ 10 ปีที่แล้ว ประเทศไทยติดตั้งอย่างเดียวไม่เน้นเรื่องการวิเคราะห์ทดสอบ ส่วนความน่าเชื่อถือเราเชื่อตามข้อมูลที่ต่างประเทศกล่าวอ้าง เมื่อ 10 ปีที่แล้วมีโอกาสได้ศึกษาเรื่องการทดสอบสมรรถนะความน่าเชื่อถือของเซลล์ 5 ชนิดในเขตร้อนชื้น ซึ่งงานนี้ได้รับรางวัลด้วย เนื่องจากญี่ปุ่น เยอรมนี อเมริกาเป็นประเทศที่ไม่ได้อยู่ในเขตร้อนชื้น เราเป็นประเทศแรกๆ ในเขตร้อนชื้นที่นำเสนองานวิจัยด้านนี้ โดยชี้ให้เห็นว่ามาตรฐานที่มีอยู่ไม่ได้สะท้อนการใช้งานจริงในบ้านเราสักเท่าไหร่นัก เพราะบ้านเรานอกจากจะร้อนชื้นแล้ว ยูวีก็แรงกว่าด้วย ดังนั้น เราจึงต้องทดสอบเพิ่มเติม
ในระยะหลังอินเดียกับสิงคโปร์มาแรงมาก อย่างสิงคโปร์เวลาที่เขาทุ่มงานวิจัยอะไร เขาก็ไปดึงทีมวิจัยจากเยอรมนีมาทำให้เริ่มได้เร็วและไปได้เร็วมาก เดิมทีในเขตร้อนชื้นอาจมีเราศึกษาวิจัย แต่ตอนนี้สิงคโปร์ที่แม้จะไม่มีพื้นที่จะติดเอง แต่เขาก็ไปเน้นแนวการวิเคราะห์ทดสอบ และก็พยายามรวบรวมข้อมูลในเขตร้อนชื้นมาทำโมเดลต่างๆ เช่นกัน
ถาม: อยากให้เล่ากรณีศึกษาที่เคยช่วยแก้ปัญหา หรือปรับปรุงระบบให้เหมาะสมตามสถานที่ต่างๆ ครับ?
ตอบ:
สถานที่ที่ทีมเคยไปมีรูปแบบที่เป็นพื้นที่โซลาร์ฟาร์มที่เป็นภาคธุรกิจจริงๆ เพื่อช่วยแก้ปัญหาระบบในการผลิตไฟฟ้า เช่น หาสาเหตุที่กระแสไฟฟ้าที่ผลิตได้มันลดลง ส่วนอีกรูปแบบคือ พื้นที่ที่ไฟฟ้าเข้าไม่ถึง เราต้องไปออกแบบว่าควรติดตั้งเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ขนาดเท่าไหร่จึงจะพอกับปริมาณไฟฟ้าที่เขาต้องการ หรือถ้าเขามีพลังงานน้ำด้วยจะมาผสมผสานเป็นระบบไฮบริดได้อย่างไรจึงเหมาะสม นอกจากนี้ในแต่ละฤดูปริมาณแสงอาทิตย์ไม่เท่ากัน หรือบางฤดูฝนตกต้องทำอย่างไร ซึ่งการใช้เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ในแต่ละพื้นที่มีลักษณะการใช้งานที่หลากหลายมากค่ะ
ถาม: แง่มุมไหนที่จะเป็นทิศทางในอนาคตที่เราจะได้เห็นความก้าวหน้าของการใช้เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ในบ้านเราหรือของโลกครับ?
ตอบ:
อยากให้มองการใช้ให้คุ้มค่าและเกิดประโยชน์เป็นหลัก ในบางแง่มุมอาจไม่ต้องเป็นระบบขนาดใหญ่ เช่น ในภาคการเกษตรที่สายส่งเข้าไม่ถึง เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สามารถช่วยเกษตรกรให้มีไฟฟ้าใช้ โดยเข้าไปทดแทนการปั่นไฟโดยใช้น้ำมัน ซึ่งการใช้เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ลักษณะนี้มีผลกระทบและมีมูลค่าการใช้งานสูง เนื่องจากเป็นพลังงานทางเลือกสำหรับกลุ่มที่มีความจำเพาะ (niche market) เราอาจไม่เหมือนญี่ปุ่น หรือเยอรมนีที่มีสายส่งครอบคลุมกว่ามาก ประเทศไทยยังมีพื้นที่ที่ไฟฟ้าเข้าไม่ถึง หากใช้เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์น่าจะเหมาะเพราะการลากสายส่งเข้าไปจะมีค่าใช้จ่ายสูงมาก
ถาม: มีข้อแนะนำสำหรับผู้ที่สนใจจะทำงานด้านเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ว่าควรไปศึกษาด้านไหนหรือต้องเกาะติดประเด็นอะไรเป็นพิเศษไหมครับ?
ตอบ:
การพัฒนาเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ต้องการความรู้หลากหลายสาขามาก เช่น ตัวเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์เป็นเรื่องวัสดุ ไฟฟ้าอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ แต่เมื่อนำเซลล์มาประกอบกันให้สามารถกันความชื้นและแสงยูวีต้องใช้ความรู้ด้านวิศวกรรม การทำให้เซลล์ติดตามดวงอาทิตย์ก็ต้องมีความรู้เรื่องมอเตอร์ การป้องกันฝุ่นเพื่อช่วยลดการสูญเสียจากการบดบังของผงฝุ่นต้องใช้ความรู้ด้านการเคลือบสาร หรือในการใช้งานจริงเมื่อโดนแสงยูวี สารเคลือบนี้จะเสื่อมสภาพหรือไม่ หรือต้องเคลือบบ่อยแค่ไหนจึงจะคุ้มก็ต้องใช้ความรู้เรื่องวัสดุ หรือการควบคุมปัจจัยต่างๆ ให้เหมาะสมเพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของอินเวอร์เตอร์ ซึ่งต้องใช้ความรู้หลากหลายสาขามาช่วยเสริมระบบให้มีประสิทธิภาพสูงขึ้นค่ะ
ขอขอบคุณ ดร.เบนซ์ที่มาให้ความรู้เรื่องเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์ รวมทั้งข้อคิดต่างๆ ในโอกาสหน้าขอเชิญมาให้ข้อมูลความก้าวหน้าใหม่ๆ ในงานวิจัยที่ศึกษาอยู่ภายใต้ศูนย์เทคโนโลยีพลังงานแห่งชาติอีกนะครับ
ผู้ที่สนใจรายการนี้ในรูปแบบพอดแคสต์ (podcast) สามารถรับฟังได้ที่